Before starting with home lab would recommend to go through with the Vsphere terminology that being used, and will talk about old version of Vmware,comparison and other things.
Previous version of Vsphere the hypervisor was available in 2 flavour ESX and ESXi.Although both flavours were from same umbrella, same license patterns and considered as bare-metal installation hypervisor. in ESX version RHEL was derives as service console to provide and interactive environmental which user could interact with the hypervisor. This service console have in built feature of firewall, SNMP agents and a web server.
on the another hand, ESXi was the nest generation of Vmware products. ESXi install and run without service console with footprint of 130MB only, with extra security and enhanced feature of ESXi.
The Vmkernal is the functionality that is found in Vmware ESXi and it was available with ESX version only.
this is small list of comparison on Vmware versions .
VMware vCenter Server: Centralized management console to manage, deploy,manage, monitor, automate, secure the virtualized infrastructure.This server not only support for management capability but also template, customization, provisioning and deployment of vms, role base access control and very fine tunes resource allocation control.It also gives admins the tools for the more advanced feature vmotion, Fault tolerance,DRS and HA.
Other features are also
1. EVC, which leverage hardware functionality from Intel and AMD to enable CPU compatibility between grouped into Vspshere DRS clusters.
2.Host Profiles, which allow to enable consistency to host configuration across larger environment to identify missing or configuration issues.
3. Storage I/O Control, which enable cluster wide QOS control, that ensure critical applications receive sufficient storage resources even time of high usage or congestion.
4.Distributed Switch, which enable the networking settings that manage multiple host and clusters.
5.Network I/O, which allow for flexible partition Physical NIC bandwidth and provide QOS for different traffic.
6.Storage DRS, which enable dynamically migrate storage resource to bring down the storage I/O's ups and down. like DRS feature in term of CPU and memory utilization.
Update Manager:.
This is advanced and add-on feature of vcenter that helps admins to update their ESXi hosts and VMS with latest updates.
1. scan the objects/system that are not up to date with latest updates
2.Automated patching of ESXi host
After Installation, it is available as plug in vcenter console and can be activated after installing in console only.
VMware vSphere Web Client and vSphere Desktop Client :
A centralized management console for ESXi host which allows nd enable admins to manage the virtual infrastructure easily.There was a major change with Vsphere 5 version with web based vsphere client. it provides web based user interface to manage a virtual infra to enable admins where Vsphere client installation was not require.
VMware vRealize Orchestrator: This was known as Vmware Vcenter Orchestrator before, work-flow which is installed with vcenter server, Using this feature, admins can create and automate workflow for different task available in VCenter list.There are other available plug-ins for further automation task in Active Directory, UCS and VRealize Automation.
vSphere Virtual Symmetric Multi-Processing: This Vmware product allow admins to create vms with multiple virtual process cores or sockets. this feature is not a licensing feature but this is a technology taht enable to use multiple process with in vm with multiple processors in the Host system and multiple virtual processors.
vSphere vMotion and vSphere Storage vMotion: Vmotion is a feature of ESXi and vcenter that allows/enable vm to moves running vm from one host to another available host. As same Storage vmotion, migrate vms from one storage to another available storage.
vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler: This is a another great feature which gives admins relief when I/O's in term of CPU/Memory fluctuating very rapidly.
vSphere Storage DRS:Just like DRS help to maintaining utilisation in terms of CPU and memory in cluster, Storage DRS helps to keep balanced performance across the data-store cluster.
Storage I/O Control and Network I/O Control:vSphere dint have feature release of vSphere 4.1.Storage I/O Control (SIOC) enable and allows admits to assign relative priority to storage I/O and limits to VMs. These settings are applied on cluster-wide. You can enable this feature
Policy-Based Storage: Admins can use storage capabilit and vm storage profiles to ensure vms on storage that provide the required capacptiy, availability and redundancy.
vSphere High Availability:We should put all our eggs in one basket! This terms well explain the HA feature.Infrastructure is more over concerned on availability of application and vms. Before this feature if physical server is down so related with that servers everything is stopped till that physical server is not up.this is an automated process for restarting vms that on running on esxi host which failed due to unexpected reason. This feature got extra and advanced enhanced feature after 5.0 vpshere version.It allows to run up to 512 VMs per host (up from 100 in older versions) and 3,000 VMs per cluster (up from 1,280 in older versions).vSphere HA integrated more closely with the intelligent placement functionality of vSphere DRS,giving vSphere HA greater ability to restart VMs in the event of a host failure. The third and perhaps most significant improvement is the complete rewrite of the underlying architecture for vSphere HA; this
entirely new architecture, known as Fault Domain Manager (FDM), eliminated many of the constraints found in earlier versions of VMware vSphere. vSphere HA does not provide failure if the issue is with guest OS or on time of failure of guest OS, admins can configure HA to monitor VMs and restart them automatically as per priority if they fail to respond to heartbeat. This feature is called VM Failure Monitoring, and it uses a combination of heartbeats and I/O activity to attempt to detect if the guest OS inside a VM be restarted automatically. Ist very important to understand the vm restart priority if HA start as we as it cam be configured that in the HA activity the vm you want to be power off on or.
vSphere Fault Tolerance:FT provides protection against host failures with no downtime. At the time of host failures, the hosts running both the primary and secondary VMs failed—vSphere HA will reboot the primary VM on another available server, and vSphere FT will automatically create a new secondary VM. As of vSphere 5.0, FT also integrated with DRS, although this feature does require
Enhanced vMotion Compatibility (EVC). Recommended by VMWARE that multiple FT virtual machines with multiple vCPUs should have 10GbE networks at hosts level.
vSphere Storage APIs for Data Protection and VMware Data Protection:another important for any infrastructure, not specific to virtual or physical infrastructure, what is the overcome policy and steps at the tme of disaster and after that.VMware vSphere 6.0 has two key components: the vSphere Storage
APIs for Data Protection (VADP) and VMware Data Protection (VDP).
VADP is a bunch or et of APIs that provide enhanced backup functionality of virtualized environments. VADP enables feature like file-level backup and restore; support for incremental, differential, and full-image backups;native integration with backup software; and support for multiple storage protocols.
vSphere Replication:This product enable data replication from a site to another site, in early version of vSphere 5.0, used at the time of only if any conjunction with VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) 5.0. vSphere Replication enables customers to replicate VMs from one vSphere environment to another vSphere environment. This means from one data-center to another datacenter. Here one site is called as production and another site is like DR site. If any issue with the primary site, admins can migrate there resource/vm to DR to minimize the impact of un wanted or accidental situation.
Now ESXi is ready in Home lab with installation only.
Make Sure vm is selected to boot with CD, or you can set in from BIOS also after BIOS setup key.
Press Continue
F11 to Accept and Continue
I added only 10 GB for ESXi installation, and here we are doing local installation. There are other different installation method. Like USB or on SAN
Root password to access the ESXi host.
Scanning means at this position ESXi installation will check HCL and minimum requirement. As you can see i gave only 2GB RAM for ESXi so its prompted me to increase.
I powered off my system and increased the RAM to 4 GB and continue to HCL checking it will start installing ESXi.
ESXi is installed and before reboot eject the ESXi bootable ISO.
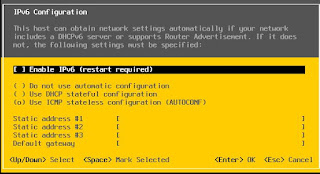
Finally ESXi is installed with automatic IP. Before starting to advanced configuration, i gave static IP, VLAN, disabled IPV6 and domain settings.
Restarted ESXi one more time.
As per basic configuration, we are done with ESXi installation.Here are lots of things to configuration.We will be updating very soon.
Previous version of Vsphere the hypervisor was available in 2 flavour ESX and ESXi.Although both flavours were from same umbrella, same license patterns and considered as bare-metal installation hypervisor. in ESX version RHEL was derives as service console to provide and interactive environmental which user could interact with the hypervisor. This service console have in built feature of firewall, SNMP agents and a web server.
on the another hand, ESXi was the nest generation of Vmware products. ESXi install and run without service console with footprint of 130MB only, with extra security and enhanced feature of ESXi.
The Vmkernal is the functionality that is found in Vmware ESXi and it was available with ESX version only.
this is small list of comparison on Vmware versions .
VMware vCenter Server: Centralized management console to manage, deploy,manage, monitor, automate, secure the virtualized infrastructure.This server not only support for management capability but also template, customization, provisioning and deployment of vms, role base access control and very fine tunes resource allocation control.It also gives admins the tools for the more advanced feature vmotion, Fault tolerance,DRS and HA.
Other features are also
1. EVC, which leverage hardware functionality from Intel and AMD to enable CPU compatibility between grouped into Vspshere DRS clusters.
2.Host Profiles, which allow to enable consistency to host configuration across larger environment to identify missing or configuration issues.
3. Storage I/O Control, which enable cluster wide QOS control, that ensure critical applications receive sufficient storage resources even time of high usage or congestion.
4.Distributed Switch, which enable the networking settings that manage multiple host and clusters.
5.Network I/O, which allow for flexible partition Physical NIC bandwidth and provide QOS for different traffic.
6.Storage DRS, which enable dynamically migrate storage resource to bring down the storage I/O's ups and down. like DRS feature in term of CPU and memory utilization.
Update Manager:.
This is advanced and add-on feature of vcenter that helps admins to update their ESXi hosts and VMS with latest updates.
1. scan the objects/system that are not up to date with latest updates
2.Automated patching of ESXi host
After Installation, it is available as plug in vcenter console and can be activated after installing in console only.
VMware vSphere Web Client and vSphere Desktop Client :
A centralized management console for ESXi host which allows nd enable admins to manage the virtual infrastructure easily.There was a major change with Vsphere 5 version with web based vsphere client. it provides web based user interface to manage a virtual infra to enable admins where Vsphere client installation was not require.
VMware vRealize Orchestrator: This was known as Vmware Vcenter Orchestrator before, work-flow which is installed with vcenter server, Using this feature, admins can create and automate workflow for different task available in VCenter list.There are other available plug-ins for further automation task in Active Directory, UCS and VRealize Automation.
vSphere Virtual Symmetric Multi-Processing: This Vmware product allow admins to create vms with multiple virtual process cores or sockets. this feature is not a licensing feature but this is a technology taht enable to use multiple process with in vm with multiple processors in the Host system and multiple virtual processors.
vSphere vMotion and vSphere Storage vMotion: Vmotion is a feature of ESXi and vcenter that allows/enable vm to moves running vm from one host to another available host. As same Storage vmotion, migrate vms from one storage to another available storage.
vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler: This is a another great feature which gives admins relief when I/O's in term of CPU/Memory fluctuating very rapidly.
vSphere Storage DRS:Just like DRS help to maintaining utilisation in terms of CPU and memory in cluster, Storage DRS helps to keep balanced performance across the data-store cluster.
Storage I/O Control and Network I/O Control:vSphere dint have feature release of vSphere 4.1.Storage I/O Control (SIOC) enable and allows admits to assign relative priority to storage I/O and limits to VMs. These settings are applied on cluster-wide. You can enable this feature
Policy-Based Storage: Admins can use storage capabilit and vm storage profiles to ensure vms on storage that provide the required capacptiy, availability and redundancy.
vSphere High Availability:We should put all our eggs in one basket! This terms well explain the HA feature.Infrastructure is more over concerned on availability of application and vms. Before this feature if physical server is down so related with that servers everything is stopped till that physical server is not up.this is an automated process for restarting vms that on running on esxi host which failed due to unexpected reason. This feature got extra and advanced enhanced feature after 5.0 vpshere version.It allows to run up to 512 VMs per host (up from 100 in older versions) and 3,000 VMs per cluster (up from 1,280 in older versions).vSphere HA integrated more closely with the intelligent placement functionality of vSphere DRS,giving vSphere HA greater ability to restart VMs in the event of a host failure. The third and perhaps most significant improvement is the complete rewrite of the underlying architecture for vSphere HA; this
entirely new architecture, known as Fault Domain Manager (FDM), eliminated many of the constraints found in earlier versions of VMware vSphere. vSphere HA does not provide failure if the issue is with guest OS or on time of failure of guest OS, admins can configure HA to monitor VMs and restart them automatically as per priority if they fail to respond to heartbeat. This feature is called VM Failure Monitoring, and it uses a combination of heartbeats and I/O activity to attempt to detect if the guest OS inside a VM be restarted automatically. Ist very important to understand the vm restart priority if HA start as we as it cam be configured that in the HA activity the vm you want to be power off on or.
vSphere Fault Tolerance:FT provides protection against host failures with no downtime. At the time of host failures, the hosts running both the primary and secondary VMs failed—vSphere HA will reboot the primary VM on another available server, and vSphere FT will automatically create a new secondary VM. As of vSphere 5.0, FT also integrated with DRS, although this feature does require
Enhanced vMotion Compatibility (EVC). Recommended by VMWARE that multiple FT virtual machines with multiple vCPUs should have 10GbE networks at hosts level.
vSphere Storage APIs for Data Protection and VMware Data Protection:another important for any infrastructure, not specific to virtual or physical infrastructure, what is the overcome policy and steps at the tme of disaster and after that.VMware vSphere 6.0 has two key components: the vSphere Storage
APIs for Data Protection (VADP) and VMware Data Protection (VDP).
VADP is a bunch or et of APIs that provide enhanced backup functionality of virtualized environments. VADP enables feature like file-level backup and restore; support for incremental, differential, and full-image backups;native integration with backup software; and support for multiple storage protocols.
vSphere Replication:This product enable data replication from a site to another site, in early version of vSphere 5.0, used at the time of only if any conjunction with VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) 5.0. vSphere Replication enables customers to replicate VMs from one vSphere environment to another vSphere environment. This means from one data-center to another datacenter. Here one site is called as production and another site is like DR site. If any issue with the primary site, admins can migrate there resource/vm to DR to minimize the impact of un wanted or accidental situation.
Now ESXi is ready in Home lab with installation only.
Make Sure vm is selected to boot with CD, or you can set in from BIOS also after BIOS setup key.
Press Continue
F11 to Accept and Continue
I added only 10 GB for ESXi installation, and here we are doing local installation. There are other different installation method. Like USB or on SAN
Root password to access the ESXi host.
Scanning means at this position ESXi installation will check HCL and minimum requirement. As you can see i gave only 2GB RAM for ESXi so its prompted me to increase.
I powered off my system and increased the RAM to 4 GB and continue to HCL checking it will start installing ESXi.
ESXi is installed and before reboot eject the ESXi bootable ISO.
Finally ESXi is installed with automatic IP. Before starting to advanced configuration, i gave static IP, VLAN, disabled IPV6 and domain settings.
Restarted ESXi one more time.
As per basic configuration, we are done with ESXi installation.Here are lots of things to configuration.We will be updating very soon.


















Better to add the abbreviations like EVC, QOS etc. Will avoid to search the details in another blogs (especially for beginners)
ReplyDeleteReally appreciate your suggestion.As VMware have lots of point, so will be covering one by one.But thanks for
Delete