In continuous of previous article where
I installed HYPER-V from power shell command, the current host will
be there in Hyper-V manager console and you can see lots of tab and
action task is listed. We will go through one by one tab with there
properties.
There are more on the HYPER-V concept
which as admins we should know and update our self. The hypervisor
running directly on the hardware with all the virtual machine
resource access serviced through the hypervisor. There are other
resources that must be available for a full functioning environment,
such as storage and networking.
Different Application and devices have
their supporting drivers for Windows, with most written by the
independent hardware vendor (IHV). All these different types of
storage and network drivers and application should be compatible with
Hyper-V environment and Operating system.
There are terms and components run in
kernel,as example VMUS which help to enable communication between
different types of hardware and services, that enable for non-cpu and
memory hardware like storage and networking. Every Virtual Service
Provide and support in responding to its virtual client.
The VMBus is not shared between all the
child partitions, and there is one channel between each child and the
parent so no communication or data can be seen by other child
partitions running on the same server. This VMBus does not incur any
significant performance penalty even though child partitions wanting
to access hardware now essentially communicate via the VSC to a VSP
on the VMBus hosted on the parent partition, which communicates to
the hardware. This is because the VMBus is actually a pure memory bus
running at a kernel level, so there is practically no latency
introduced, and by using this model, Microsoft keeps the hypervisor
small and secure while still allowing full hardware support for the
breadth of the Microsoft hardware ecosystem.
SCSI Controller :Generation 1
virtual machine does not have a SCSI controller, but up to four SCSI
controllers can be added to a virtual machine. Once a virtual machine
has four SCSI controllers,then option to for SCSI controllers will be
grayed out.
In-memory VMBus, SCSI controller is the
device which gives essentially the highest, bare-metal storage
performance. The term bare-metal indicate for a system or environment
that does not use virtualization. oar a non-virtualized environment,
Each SCSI controller supports up to 64 hard drives attached, maximum
of 256 disks attached via the SCSI bus.
The SCSI controller functionality is
more enhanced in Windows Server 2012 R2 like Shared VHDX between
multiple virtual machines and Dynamic re-sizing of VHDX.
This Pic will clear the difference
between Generation 1VM and Generation 2VM versions.
The following Server operating systems
can be installed in a generation 2 virtual machine:
>Windows Server 2012
>Windows Server 2012 R2
Conversion of Virtual Machine from
Generation from 1 to Generation 2 is bit difficult due to different
constraints because generation 1 virtual machine is BIOS based, which
equates to a certain disk configuration such as an NTFS system
partition. A generation 2 virtual machine is UEFI based and uses a
FAT32 system partition. This alone prohibits moving virtual hard
disks between generation 1 and generation 2 virtual machines. Also
remember that generation 1 machines boot from the IDE controller and
generation 2 machines boot from the SCSI controller. The only way to
move from generation 1 to generation 2 is to boot the virtual machine
from Windows PE, capture the partitions to a WIM fi le, then redeploy
to a generation 2 virtual machine,but this amount of effort is really
not worth the benefit t, and generation 2 is best saved for new
virtual machines.
Windows Server 2012 R2 Hyper-V has
another processor-related setting that is set on a
per-virtual-machine basis. This setting is migrate to a physical
computer with a different processor version. It is not possible to
migrate a virtual machine between Intel and AMD processors using
migration technologies due to the completely different architecture
and instruction sets of the processor.
To resolve this problem, Hyper-V adds
the ability to hide many higher-level functions of processors in the
guest operating systems. This means you can move guest operating
systems between nodes in a cluster even if the processor versions are
different because the virtual operating systems are exposed only to
the generic instructions that are present in all versions of the
processor family. Note that the functionality does not scan the
processors and expose the lowest common set of functionality of all
the processors in the cluster; it just limits to a generic basic set.
This can also be set using Power Shell
with the following
command:
Set-VMProcessor
-CompatibilityForMigrationEnabled $true
Prior to Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V,
there was also a setting to enable running older operating systems
such as NT 4, but this option has been removed from the Hyper-V
manager graphical user interface. The problem for older operating
systems is that modern processors return more information about the
capabilities than can be handled by the operating system and it will
blue screen (this was fi xed in Windows NT 4.0 SP6). This option can
still be set, but it must be configured using Power Shell:
Set-VMProcessor
-CompatibilityForOlderOperatingSystemsEnabled $true
A great way to understand these two
settings is with the help of the Core info utility from SysInternals,
which can list all features for a processor. You will find it at the
following location:
Windows Server 2012 introduced a new
set of configurations for virtual machine processors,NUMA, but the
reality is you should never touch these. Most likely bad things will
happen and Hyper-V will make the right configurations for your
environment without any manual intervention. This NUMA awareness is
also a benefit t for enterprise applications such as SQL, MySQL, and
IIS that utilize resources based on NUMA configuration.
A VHD can be up to 2 TB in size, and
there are a number of different types of VHDs available:
1.Dynamically expanding: This is the
most popular format. Essentially the virtual hard disk is created
using a minimal amount of disk space, and as the disk is used, the fi
e expands on the fi le system to accommodate the data written to the
disk up to the size specified as the size for the virtual hard disk.
This option is the most efficient use of the disk space because space
is not used on the physical hard drives unless needed. In Windows
Server 2008, there was a performance penalty with dynamic disks, such
as when a write was performed, the file had to grow. However, the VHD
implementation was rewritten in Windows Server 2008 R2, and this
performance penalty is negligible. A dynamically expanding disk
doesn't shrink if data is deleted unless a compact operation is
performed. this type of disk is also commonly refereed to as thinly
provisioned because it start off thin and grows as data is written to
it.
2. Fixed Size: the size specified for
the virtual disk is also to user when the disk is created and so if a
127 GB fixed size virtual disk is created, a 127 GB vhd is created on
the hyper-v sever. this is likely to lead to less fragmented virtual
hard disk
3. Differencing: a differences disk is
linked to a parent virtual disk and only store the changes from the
parent disk.
Will create one vm with no os version
just to see the tabs, option under properties.
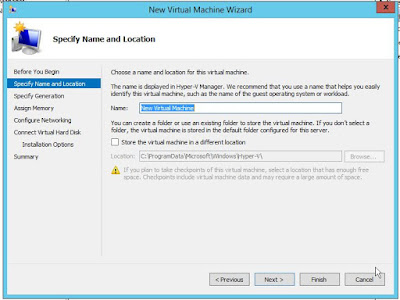
started creating vm on this
hypervisor by right click and create new vm
her you can specify name and location
of the vm, where you wan to save files of newly created vm.
This screen well explain about
difference in generation-1 and generation-2 type of vm. There is a solution also to change the Generation from 1 to 2.
memory allotment can be done from here
This wizard help you for disk related
task like you can create new or add existing disk to vm from this
option.
This option help you to install OS on
the vm. you can see in the below of screen shot, it give warning of
network adapter because I didnt configured my Hyper-V network stuffs
yet :) as this option would need network connection.
here it will show all vm that are with
this hypervisor host or vms managed by this hypervisor host.







No comments:
Post a Comment